Effects of Additives on Properties of Al in Alkaline Colloidal Electrolytes
2021-05-02
Abstract : The effect of additives PVA and Na3PO4 on the electrochemical performance of aluminum anodes was studied electrochemically in "4 mol/L KOH+20% polyacrylic Acid (PAA)". When adding 2% PVA or 8% Na3PO4 Additive, just "4mol/LKOH+20% PAA" can be made into a colloid. Compared with the “4mol/L KOH+2 5% PAA” colloidal electrolyte, the corrosion current density and polarization degree of aluminum decrease, the open circuit potential shifts negatively, and the conductivity and discharge time increase. The electrochemical performance of 8% Na3PO4 on aluminum is more obvious than that of 2% PVA.
Key words: aluminum anode; alkaline colloidal electrolyte; additive; electrochemical performance
CLC number: TM911 41 Document code: A Article ID: 1001-1579 (2006) 03-0214-02
The characteristics of acidic colloidal lead-acid batteries [1] have aroused great interest, but there are few reports on the basic colloidal electrolytes. Aluminum air battery has many advantages [2], 25% polyacrylic acid (PAA) can just make 4mol/LKOH colloid, and the corrosion of aluminum is small, but compared with the free base solution, the degree of polarization of the aluminum anode increases [3] Because the PAA content affects electrolyte diffusion, its content should be reduced. The author of this paper reduced the concentration of PAA to 2%, and used polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) and Na3PO4 as additives to study the performance of aluminum anodes in alkaline colloidal electrolytes.
1 experiment
Electrode: 1 The study electrode was aluminum (99 999%, helium 100mm). One end of the electrode was exposed, and the rest was sealed with epoxy resin. The 1200#, 2000#, and 3000# metallographic sandpaper were used to polish and then degreasing with ethanol. 2 The auxiliary electrode is graphite; 3 reference electrode is HgO/Hg, 4mol/LKOH. Reagents: KOH, Na3PO4 (AR), PAA, PVA (industrial products). Instrument: The linear scan voltammogram (1mV/s), Tafel curve (1mV/s), potential change curve, and open circuit potential Eocp of the aluminum anode were measured with LK98BII (Tianjin); alkaline colloids were measured with CHI660A (USA) Electrolyte conductivity. The experimental temperature is 30°C.
2 Results and Discussion
2 1 Effect of additive PVA 2 1 1 Corrosion performance
FIG. 1 is a Tafel plot of Al in “4 mol/L KOH+2% PAA+x% PVA”.
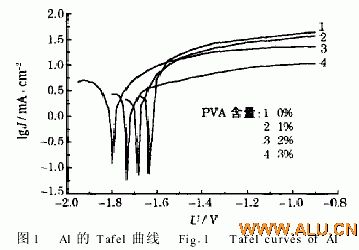
Obviously: 1 With the increase of PVA content, the corrosion current density of aluminum decreases. This is because the polymer PVA hinders the diffusion of water during hydrogen cathode reduction, and the self-discharge of the aluminum electrode will be significantly reduced; 2 when it becomes a colloid The corrosion rate of the colloidal electrolyte "4mol/LKOH+2%PAA+2%PVA" (Jcorr=4 75mA/cm2) is lower than that of the colloidal electrolyte "4mol/LKOH+25%PAA" (Jcorr=509mA/cm2). Table 1 shows.
2 1 2 Polarization degree and open circuit potential In the “4 mol/L KOH+2% PAA” solution, the degree of polarization of aluminum increases with increasing PVA content of the additive (see Figure 2a).
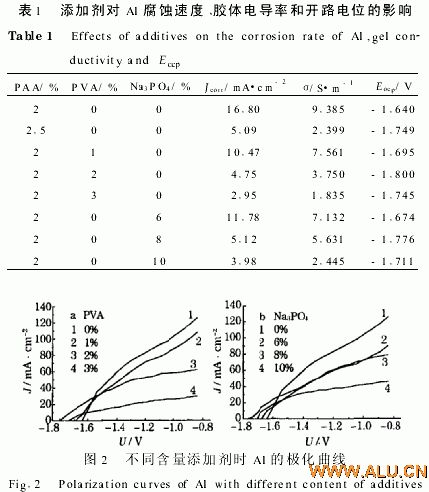
This may be due to the fact that high-molecular additives will make the electrotransport of K+ and OH− difficult, but too little addition will affect gelation. Just when the "4mol/L KOH + 2% PAA" solution is colloid, the preferred concentration of PVA is 2%; at the same time PVA makes the open potential of aluminum negative shift, and aluminum is "4mol/LKOH + 2% PAA + 2% The open circuit potential in PVA" is negatively shifted to a greater degree (see Table 1).
2 1 3 Conductivity and potential changes
The colloidal conductivity decreases with increasing PVA content (see Table 1); at the same time, the conductivity ratio is just “4 mol/L KOH+2% PAA+2% PVA” when compared to “4 mol/L KOH+2 5% PAA” "The colloidal conductivity is greater.
For J=75mA/cm2, the effect of PVA on aluminum potential is shown in Figure 3. PVA can improve the performance of colloidal electrolyte, aluminum electrode potential is negative
2 2 Effect of Additive Na3PO4
2 2 1 Corrosion performance The effect of additive Na3PO4 on the corrosion rate of Al (in “4 mol/L KOH+2% PAA”) is shown in Table 1.
Obviously: 1 With the increase of Na3PO4 content, the corrosion current density of aluminum decreases; 2 When the colloid is just formed, the corrosion rate of 8% Na3PO4 colloidal electrolyte ("4mol/LKOH + 2% PAA") (Jcorr = 5 12mA/ Cm2) is almost equal to 25% APP colloidal electrolyte (4 mol/L KOH) (Jcorr=509 mA/cm2).
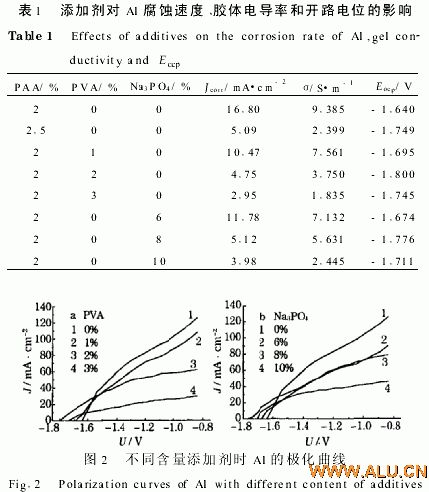
2 2 2 Polarization degree and open circuit potential As the content of Na3PO4 increases, the degree of polarization of aluminum increases (4 mol/L KOH+2% PAA) (see Fig. 2b). This may be because as Na3PO4 increases, its ability to adsorb K+ and OH- increases, but too little addition will affect gelation. The preferred concentration of "4 mol/L KOH + 2% PAA" solution as colloid is 8%; meanwhile, Na3PO4 negatively shifts the Eocp of aluminum, and Al is the Eocp of "4 mol/L KOH + 2% PAA + 8% Na3PO4". The degree of negative shift is larger (see Table 1).
2 2 3 Conductivity and potential changes
The Na3PO4 content increased and the colloidal conductivity decreased (Table 1), making the conductivity of “4 mol/L KOH+2% PAA+8% Na3PO4” colloid larger than that without the additive. When J=75 mA/cm2, the effect of Na3PO4 on the aluminum potential is shown in Figure 3. In the colloidal electrolyte Na3PO4 can improve the performance of Al anode and improve the discharge performance of aluminum.
Table 2 shows the effect of different additives on the electrochemical performance of Al anodes.
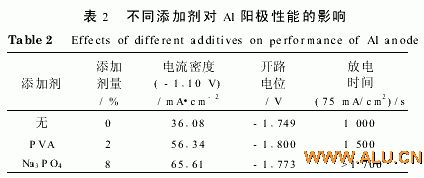
The colloidal electrolyte containing 2% PVA and 8% Na3PO4 additive ("4 mol/L KOH+2% PAA") is more effective than no additive in terms of polarization (see Figure 2), open circuit potential, negative shift of electrode potential, and discharge time. "4 mol/L KOH + 2 5% PAA" was significantly increased. Na3PO4 works well.
3 Conclusion
Adding 2% PVA and 8% Na3PO4, respectively, can just make "4mol/LKOH+20%PAA" colloid, compared with "4mol/LKOH+25% PAA" colloidal electrolyte, the electrochemical performance of aluminum is larger. Increase; In addition, the electrochemical performance of 8% Na3PO4 on aluminum is more obvious than that of 2% PVA.
If you want to know more about the products in Effects of Additives on Properties of Al in Alkaline Colloidal Electrolytes, please click the product details to view parameters, models, pictures, prices and other information about Electrolyte Additive,Iodine Crystal Granule Crystal,Iodine Crystal,Cas 7553-56-2.
Whatever you are a group or individual, we will do our best to provide you with accurate and comprehensive message about Effects of Additives on Properties of Al in Alkaline Colloidal Electrolytes!
Electrolyte Additive, Iodine Crystal Granule Crystal, Iodine Crystal, Cas 7553-56-2
Leonardite Source Humate Co., Ltd. http://www.hnionicliquids.com





